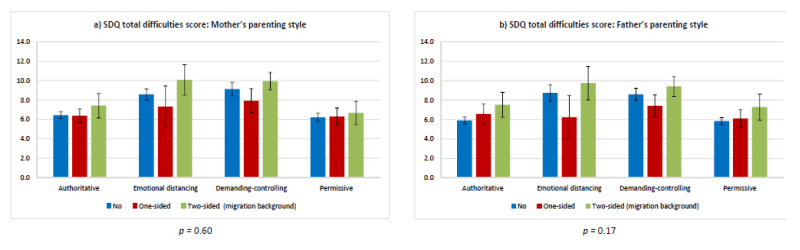
Physical Development During Childhood – Children’s experiences affect how their brains work, how they respond to stress, and their ability to build confidence. In recent years, the brain has experienced its greatest development, becoming the basis for social and emotional development. Language develops, motor skills develop, thinking becomes complex, and children begin to understand their own and others’ feelings.
From the first day of life to the first day of school, a child grows at a different pace.
Physical Development During Childhood
All aspects of child development are interconnected (Figure 1.1). For example, a child’s ability to learn new information is affected by his ability to interact with others and his ability to control his immediate emotions.
Developing Motor Skills. Concept Of Promoting Physical Development In Early Childhood By Gymnastics And Sports Stock Photo, Picture And Royalty Free Image. Image 33786094
In Shelby County, the CANDLE study collected biological, physical, and behavioral data to help us better understand these connections and their overall impact on children’s lives. health.
Social and emotional development is a change in a child’s ability to respond and interact with his environment over time.
Social and emotional development is complex and successful in many different areas. Each is explained in detail below:
1.2. Figure 1 shows examples of children’s main social and emotional skills. Children grow in all areas of development from birth to four years. These key points help us determine if children are growing “on time.” They also help us understand what children should understand and do at that age.
Characteristic Features Of Physical Development
Have you ever noticed that children have their own personality from the day they are born? Nature is the beginning of character. It is mostly about how a child acts and reacts to different situations and how it interacts with caregivers and strangers. Most children fall into one of three temper tantrums: easy, slow to warm, and hard.
Because children have different personalities, parents and other caregivers must learn to create an environment that supports their children’s well-being.
Nationally, more than half (55 percent) of infants have at least one period difficulty, indicating that these characteristics are common (Figure 1.3). For example, babies often need attention and business. However, if the child seeks attention by crying excessively, fits or whimpers, this may indicate anxiety. And this behavior makes parenting difficult for many parents. In fact, 22 percent of babies have two or more of these symptoms.
Source: Early Childhood Longitudinal Study, Birth Cohort (ECLS-B), 9-month data wave (2001-2002), parent-reported children with “frequent” symptoms.
Pdf) Physical Growth: Is It A Good Indicator Of Development In Early Childhood In Low And Middle Income Countries?
Source: Early Childhood Longitudinal Study, Birth Cohort (ECLS-B), 9-month data wave (2001-2002), parent-reported children with “frequent” symptoms
The ability to form attachments is present from birth and plays two important roles in children. First, it encourages children to stay close with a caregiver who protects them. Second, it allows children to rely on their caregiver for support as they explore their environment. Children who do this successfully are often referred to as “secure attachments.”
Children learn social skills early, which determines their intelligence. For example, children make eye movements, follow faces, and respond to sounds. As children grow, they interact with other children and adults, which helps them learn more about relationships.
Nationally, the percentage of high-risk infants in the Early Family and Childhood Survey (BABY FACES) is 90 percent of the relationship between a year.
Growth & Development
Using the same measure, in Shelby County, parents of more than three-fourths (78 percent) of the 12-month-old children who participated in the CANDLE study were considered competent.
Source: Candle Study (2009-2012) Parent-report of social competence as measured by the Early Childhood Assessment of Children (BITSEA)
Emotional regulation is the child’s ability to control his thoughts and feelings towards the environment. This does not mean that the child should be happy, brave and patient. For example, it is difficult for crying children to communicate their needs, or for children to throw tantrums and overstep boundaries. But some children are very sad.
One theory suggests that the greatest progress in cognitive development can be made during the period with children, who are at greatest risk for social problems and perspective (Figure 1.4).
Physical Growth In Middle Childhood
In addition, this theory suggests that this approach makes the community or society less profitable in the long run. Pay now or pay more later. Unfortunately, many children struggle with at least one area of social and emotional development. These children and communities can benefit from investing in giving them the best possible chance. But we need to know who works, for whom, under what conditions, where and how much to invest.
In the next chapter, A Good Start explores the issue of social and emotional development in more detail and provides insight into how we can all contribute.
There is no “one size fits all” approach. Good Start has some quick tips on supporting children’s social and emotional development, but it’s important to review the evidence when choosing a program to use. is more right.
This book is designed to help understand the social and emotional needs of children in Shelby County and to help community members think about how they can make a difference.
Middle Childhood Timeline
To do this, the report provides information from both local and national sources. A list of these resources can be found in Appendix A. Using local and national data on the experiences available in Shelby County on health and mental health development, identify examine the differences and similarities between our local communities and America as a whole, and highlight areas where more information is needed to better understand local issues. Physical development, also known as gross and fine motor development, ranges from close to central, head to toe, and simple to complex. It’s a process that starts from a person’s childhood and continues into adulthood, focusing on all good driving skills. Physical development includes the control of the body such as muscles and coordination of the body. As children learn what their bodies are capable of, they begin to gain self-confidence, promoting social and emotional development. Infancy is an important time for the development of brain and body coordination, making it easier for certain activities such as holding, crawling, walking and writing. Children learn many skills through practice and repetition.
This is a time of rapid growth that builds on the foundation of pregnancy growth. Before the umbilical cord is cut, the baby must breathe and breathe. In the first year and a half, they add motor skills such as rolling over, lifting their head, reaching for things, sitting, crawling and taking their first steps. Motor skills begin to appear in an order, followed by cephalocaudal and proximodistal trends. The cephalocaudal pathway is a vertical line of intellectual development, starting from the head down. Babies first learn to control their head, then their shoulders and body, and then their legs. The proximodistal difference is an internal competition between the motor and the growth of the body, with growth towards the outside of the spine. Children first learn to control their hands, then their hands, and finally their fingers.
Many major changes occur in all fine motor skills. Gross motor activity includes movement in the environment such as walking, running, jumping, rolling, jumping, climbing, and swinging. Fine motor skills often include more limited, controlled and precise hand movements, such as drawing, writing, cutting with scissors and handling small objects. During this year, children begin to learn many motor skills, such as riding a bicycle or throwing and catching a ball. Over time, they began to learn some driving skills.
At this stage, children show growth in height and weight, but not regularly. Children start losing the first 20 teeth one by one, they are replaced by permanent teeth. Girls have been shown to grow faster than boys, get permanent teeth sooner and develop bone growth earlier. Children at this age develop their fine motor skills. Their drawings are more detailed and mature, and their writing is smaller and smoother.
Physical Development In Early Childhood
In childhood, children should pay attention to their bodies. In many cultures, a person’s physical attractiveness is associated with his self-esteem.
At this stage, the beginning of puberty is a visible change in the body. Adolescence is a time of hormonal changes as well as a growth spurt. Hormonal release includes bone density, facial oil, and sweat production.
At the age of 15 for girls and 17 for boys, growth stops and children reach adulthood. At that age, they feel comfortable in their own skin. When they reach sexual maturity, they are more interested in intimacy and sex, including kissing, caressing and sometimes