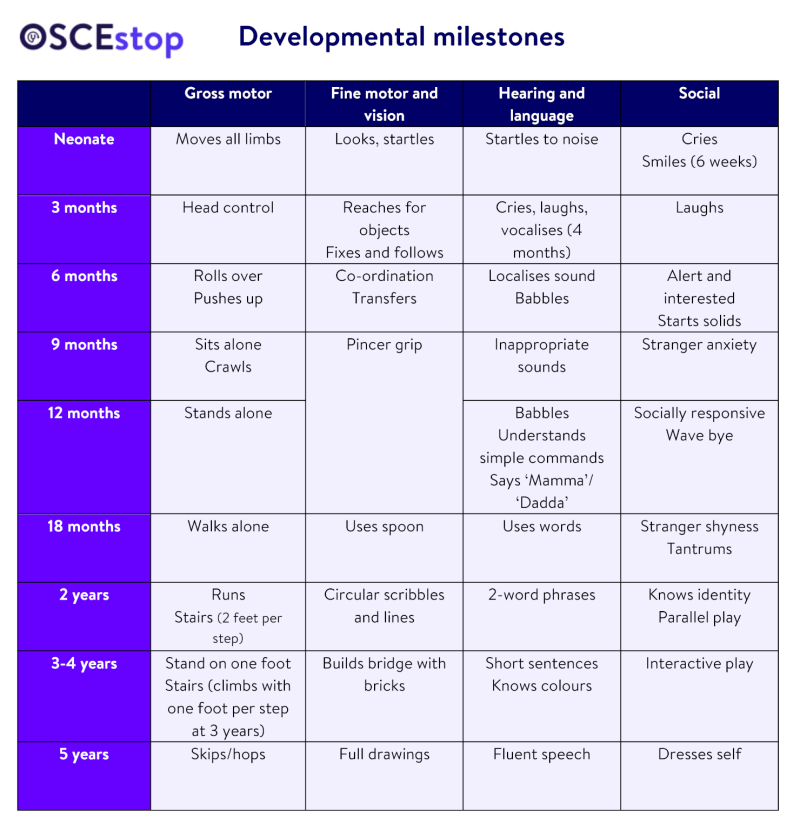
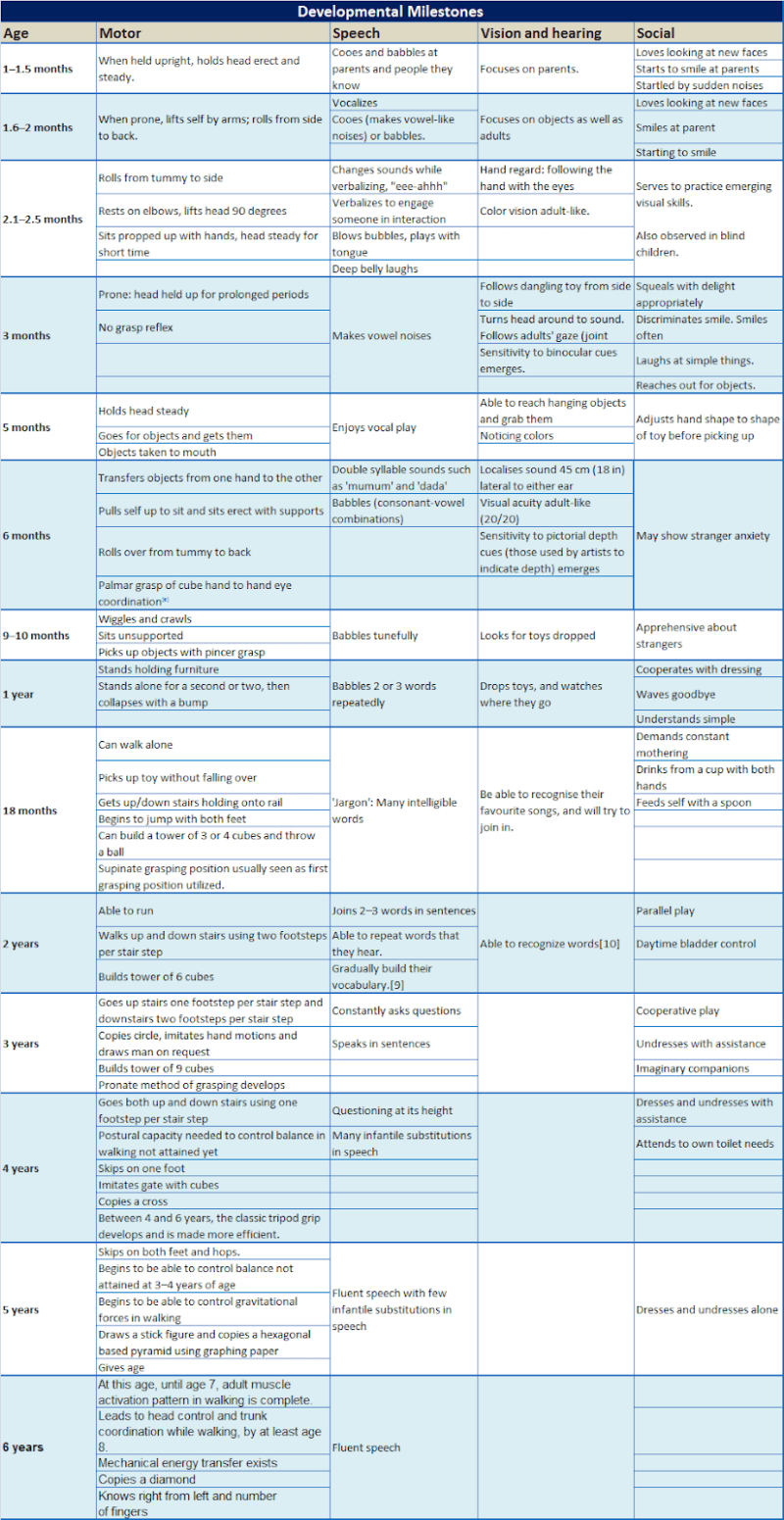
Authoritative Parenting Style – A psychologist explains 4 types of parenting. How to find the right style for you
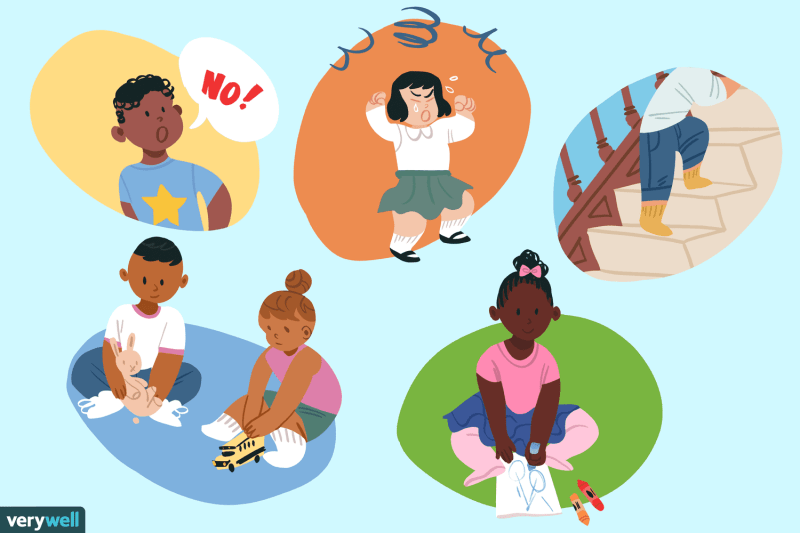
Because children don’t come with manuals, parents often find it difficult to decide how to raise mentally strong, well-rounded, and successful children. Some parents are strict, others are gentle. Some are alert while others are aloof.
Authoritative Parenting Style
“What kind of parent do I want to be?” always comes to mind, it helps you understand the basics of different parenting styles.
Authoritative Parenting Examples (2023)
The four main parenting styles—permissive, authoritarian, passive, and authoritarian—used in child psychology today are based on the work of developmental psychologist Diana Baumrind and Stanford researchers Eleanor Maccoby and John Martin.
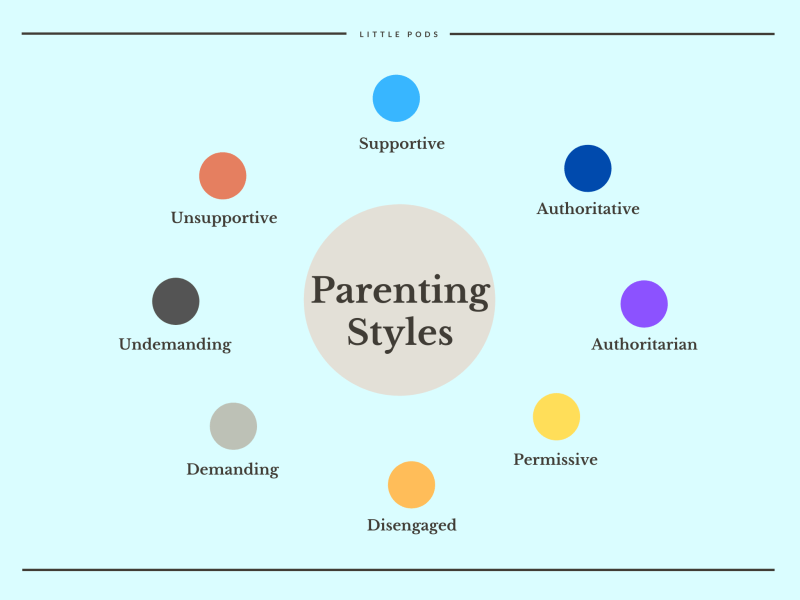
Each parenting style has different effects on children’s behavior and can be characterized by certain characteristics as well as the degree of responsiveness (the degree to which parents are warm and sensitive to their children’s needs) and demanding (the degree to which the mother is controlling ) differentiate. fathers their children). to influence their behavior).
Permissive parents take on a friendship role with their children rather than a parenting role. They prefer to avoid conflict and often give in to their children’s requests at the first sign of distress. These parents allow their children to do whatever they want and offer limited guidance or guidance.
Good parents are caring, supportive, and often responsive to their children’s needs. They guide their children through open and honest conversations to instill values and reasoning. Children with authoritative parents tend to be self-disciplined and think independently.
Authoritative Parenting Archives • Pyramid Psychology
This style is sometimes called abstract parenting and is characterized by general indifference. Neglectful parents have limited involvement with their children and rarely enforce rules. They can also appear cold and unfeeling – but not always on purpose, as they are often struggling with their own problems.
This strict parenting style is based on strict discipline, often justified as “tough love.” In an effort to gain complete control, authoritarian parents often talk to their children without asking for input or feedback.
While children of authoritarian parents are not immune to mental health problems, relationship difficulties, substance abuse, lack of self-control, or low self-esteem, these characteristics are more common in children of parents who adopt an authoritarian parenting style.
Of course, when it comes to parenting, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. You don’t have to focus on just one type, as you may need to use different training methods – but in moderation.
Do You Know Your Parenting Style?
The most successful parents know when to change their style depending on the situation. For example, an ideal parent would want to be more lenient when a child is sick, continue to provide warmth, and relinquish some control (e.g., “Sure, you can eat ice cream for lunch and dinner.”).
And permissive parents may be more assertive when the child’s safety is at risk, such as when crossing a busy street (e.g., “You’re going to hold my hand whether you like it or not.”).
In the end, use your best judgment and keep in mind what parenting style is best for your family
Francyne Zeltser is a child psychologist, school psychologist, assistant professor and mother of two children. She promotes a supportive approach to problem-solving in which her patients learn adaptive strategies to overcome challenges and work to achieve short- and long-term goals. His work has been shown in
The Four Parenting Styles And How They Influence Development
Local to your neighborhood Listen: NBC 7 Podcast NBC 7 Community Answers NBC 7 Down to Earth with Dagmar Military Weather Investigations Discussion Politics Submit Tips California SportsWrap San Diego Padres US video and entertainment in your California neighborhood Live, worth the trip
About us Our news Standards Submit user complaints Submit photo and video contests Our app newsletter Cozi TV “Four categories define parenting styles based on variations on two main factors: warmth (responsiveness) and control (needs).” ↓ Share SHARE Share Facebook TWEET Share Twitter PIN IT Share Pinterest
What kind of parents are you? In the field of psychology, experts today distinguish four different parenting styles: authoritarian, authoritarian, permissive and careless. These different approaches have unique strengths and weaknesses. Let’s look at how each style affects children and can influence their risk of anxiety.
In the 1960s, psychologist Diana Baumrind conducted research on 100 preschool children and their parents and, based on her observations, distinguished between three different parenting styles (authoritarian, authoritarian, and permissive), to which psychologists Eleanor Maccoby and John Martin then added a fourth category . (Default). or irrelevant). Four categories define parenting styles based on variations on two main factors: warmth (responsiveness) and control (demanding). Authoritarian parenting is characterized by a high degree of control and little warmth. Both factors were affected by forced parenting. Permissive parenting has little control but lots of warmth. And in both cases, parental neglect was minor. The characteristics of each parenting style are described below:
How Parenting Styles Affect Child Development
Authoritarian parenting is characterized by a high degree of control and little warmth. By taking on the role of disciplinarian, authoritarian parents demand respect while simultaneously emphasizing obedience. They are often strict and punitive, requiring their children to follow orders without question. This type of parent usually uses phrases like “Do as I say, not as I do” or “Because I say so.” Although they criticize a lot, they rarely praise or express affection, which often leads to children being less likely to do so become independent and afraid of their parents.
When it comes to forced parenting, warmth and control are particularly important. In addition to maintaining a supportive and nonjudgmental environment, parents can also exercise control and guidance through appropriate boundaries and discipline. Custodial parents want their children to become independent individuals, and they often see compromise as the best way forward. Children are allowed to express their own opinions as long as they do so respectfully.
Permissive parenting has little control but lots of warmth. Without many established boundaries, children can do whatever they want without fear of discipline. Permissive parents don’t want to disappoint their children and love the idea of being their child’s best friend.
And with neglectful parenting there is a lack of warmth and control. Without involvement and little support, neglectful parents show little love and affection for their children and little guidance. Because there is little structure at home, neglectful parents often have a distant relationship with their children because the children learn that they cannot rely on their parents for support.
Authoritative Vs Authoritarian Parenting
Since Baumrind first published her study, many studies have been conducted on the positive and negative effects of different parenting methods on children. Here are the pros and cons of each style, as identified by experts, starting with the one considered the most dangerous:
The general consensus about parental neglect is that it has a negative impact on children. This type of parent is so uninvolved in their children’s lives that they hardly demand it, but do not show them love or affection. While this parenting style can lead to a child having a more independent attachment style, which can be a positive outcome, children who are neglected often have low self-esteem and poor social skills because they have not learned to interact with their mothers in a healthy way . Father . This can also cause them to become more emotionally needy or distant in future relationships. It’s important to note that sometimes neglectful parenting is unintentional and is a direct result of a parent working too much or struggling with a mental illness or substance abuse problem. Parents can also be negligent because they were raised by negligent parents. Parental neglect should also not be confused with the initial distress or separation that the mother may feel in the postpartum period, during which she is encouraged to speak to a doctor to address her concerns.
Authoritarian parents set high standards and demand adherence to them, which gives children the structure they need and can cause them to be very goal-oriented and determined to do “the right thing.” But authoritarian parents’ lack of warmth and care for their children can lead to rebellion and resentment toward strict parenting. Children of authoritarian parents often have low self-esteem, poor social skills, and high levels of depression because they never felt free to express their own opinions or stand up for themselves. When harsh punishments are used at home, these children may also be vulnerable to violence or aggression toward their peers or later in life. Children of authoritarian parents are also less creative because they are always taught to accept rules and not to think outside the box.
Permissive parents don’t ask much of their children, but show them a lot of love. Although this type of parenting includes warm and loving behavior toward children, it also lacks the discipline, boundaries, and standards necessary for behavior and academic success. Although children with permissive parenting may have higher self-esteem, emotional closeness to their parents, and a greater willingness to be creative, they may also engage in risky behaviors. You can also show disrespect