Types Of Parenting In Psychology – A psychologist explains 4 types of parenting. Here’s how to determine which style is right for you
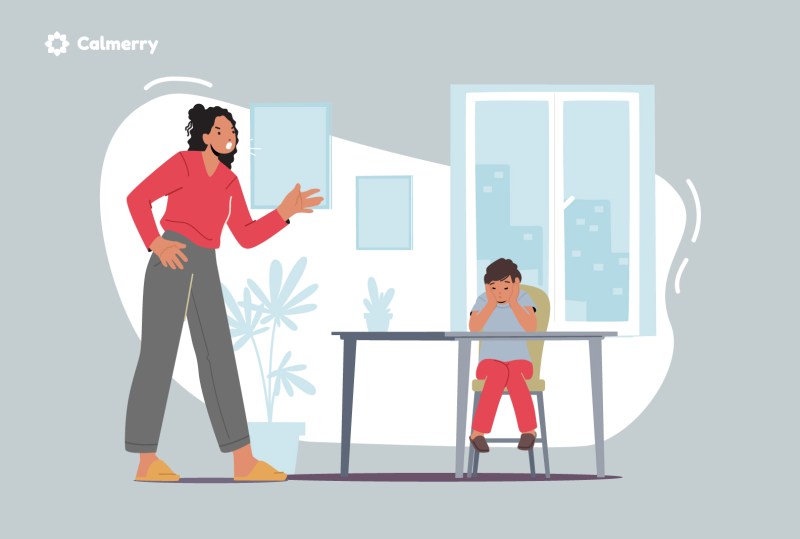
Because children carry manuals with them, parents often struggle to decide how to raise mentally strong, talented, and successful children. Some parents are strict, others are lax. Some are active, others are distant.
Types Of Parenting In Psychology
“What kind of parent do I want to be?” will come to mind, helping you understand the basics of different parenting styles.
Mnemonic Devices: Types, Examples, And Benefits
Four basic parenting styles—permissive, authoritative, neglectful, and demanding—are used in child psychology today in the work of Diana Baumrind, a developmental psychologist, and Stanford researchers Eleanor McCoby and John Martin.
Each parenting style has a different effect on children’s behavior and can be characterized by certain features, as well as the degree of responsiveness (parents are warm and sensitive to the needs of their children) and self-confidence (parents have control over their children’s behavior) .
Volunteer parents are more likely to take on a friendship role than a parenting role with their children. They prefer to avoid conflict and often give in to their children’s requests at the first sign of fear. These parents usually let their children do what they want and provide some guidance or direction.
Authoritative parents are attuned to their children’s needs, supportive and often supportive. They guide their children through open and honest discussions and teach them values and rationality. Children with authoritative parents are often disciplined and can think for themselves.
A Psychologist Shares The 4 Types Of Parenting—here’s The Most Successful Style
This style, also called uninvolved parenting, is characterized by a general sense of indifference. Neglected parents have limited contact with their children and do not follow the rules. They can also be seen as cold and uncaring, but not always intentionally, as they often struggle with their own problems.
This strict parenting style often uses harsh discipline, which is called “tough love.” To maintain complete control, authoritarian parents often talk down to their children without waiting for input or feedback.
Although children of authoritarian parents are less likely to have psychological problems, relationship problems, substance abuse, poor self-control, or low self-esteem, these traits are more common in children with authoritarian, permissive, or uninvolved parenting styles. .
Of course, there is no ‘one size fits all’ when it comes to parenting. You can sometimes use different parenting styles, so you don’t have to choose just one type of parenting, but in moderation.
Best Parenting Books 2023
The most successful parents know when to change their strategy depending on the situation. For example, when a child is sick, authoritative parents continue to keep them warm and relinquish some control (e.g., “Sure, you can have ice cream for lunch and dinner”).
And when the child’s safety is at risk, the permissive parent can be even stricter, such as when he interrupts aggressively (e.g., “You’re going to hold my hand whether you like it or not”).
At the end of the day, make a decision and remember which parenting style works best for your family
Francine Zelser is a child psychologist, school psychologist, university teacher and mother of two children. She promotes a supportive problem-solving approach in which her patients learn adaptive strategies to cope with challenges and achieve short- and long-term goals. Her work stands out
The Four Styles Of Parenting
LISTEN NEARBY: NBC 7 Podcasts NBC 7 Answers NBC 7 Community Earth with Dagmar Political Talk Military Weather Investigative Tip California Sports Pack San Diego Padres US and World Videos Entertainment Near You California is worth the trip
Submit a consumer complaint about our news criteria Submit photo and video contests Our program newsletter Cozi TVInside: 4 parenting styles in developmental psychology and why they are important for independent parenting Why gentle parenting or positive parenting are not the same as tolerant parenting. A balanced approach is best.
As much as we would like this to be true, unfortunately children are not born with instructions on their hands. As parents, we need to figure out how to raise good, successful children.
If you’re wondering what kind of parent you want to be, this article is a good place to start. The key to figuring out your parenting style is to understand the four parenting styles of developmental psychology.
What’s Your Parenting Style?
The four parenting styles of developmental psychology are based on the work of the late psychologist Diana Baumrind in the early 1960s. Dr. Bamrind and Stanford researchers Eleanor McCoby and John Martin found that each parenting style affects a child’s behavior differently and falls into two dimensions or categories: responsiveness and curiosity.
Recently, psychologists have identified a third dimension—structure—the degree to which parents provide their children with a predictable, organized, and consistent environment.
Accountability, questioning, and structure create a rich relationship between you and your child. Here are 4 parenting styles and their main characteristics and their importance for children’s development.
Parents with an authoritative parenting style solve problems together with the child. Instead of letting their child figure it out for themselves, they get down to their level and help them come up with ideas to solve the problem. You don’t give them the answers, you give them the tools to work with when they are available. These children often have self-discipline and can think for themselves when conflicts arise.
Pdf) Parenting Styles: A Closer Look At A Well Known Concept
Authoritative parents set clear rules and expectations for their child. They have clear boundaries and rules and communicate with their child in a way that promotes cooperation by offering choices, suggestions and encouragement.
One of the most important characteristics of an authority style is an open line of communication and natural consequences. Although there are clear rules and expectations, the child and parent should always talk about their needs, communicate with each other and work together in all areas. These natural consequences occur when parents make their child do something they know will happen next time.
Authoritative parents use discipline to teach and solve problems, not as punishment. It promotes the child’s independence.
This parenting style is very controlling and supportive. Authoritative parents also have a tendency.
Histrionic Personality Disorder: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
For my children. Parents respond to their child’s social and emotional needs and provide clear rules and expectations.
One study found that parents who used authoritative parenting practices had children with better measures of social and emotional development (such as play, self-esteem, anger, interpersonal relationships, transitions, and behavior). Another study found that children of authoritative parents had higher academic achievement and adjusted better in college.
An authoritarian parenting style focuses on the parents, not the child. This means that parents will set strict rules and sanctions if these rules are not followed. Parents expect the child to listen and do not demand an answer from the child. They are the authority figures, and the child’s behavior should reflect that.
In authoritarian parenting styles, the lines of communication are often one-way. The child’s social and emotional needs are not a priority and the most important thing is that the child obeys the rules and demands of the family. Less flexibility in meeting the child’s needs and less support, warmth and encouragement from parents.
Why Psychologists Say ‘positive Parenting’ Is The Best Style For Raising Confident, Successful Kids
The authoritarian parenting style consists of a lot of control, little support and a very high structure. Parents in this style expect obedience from their children and ignore their children’s emotional and social needs.
Longitudinal and cross-cultural studies show that harsh discipline predicts later behavioral problems and lower self-esteem. In Japan, authoritarian parenting styles predict poorer mental health (e.g., symptom problems, danger to self and others, life functioning, and psychological well-being) later in life.
Parents who use this parenting style are sometimes called neglectful parents because they are not involved with their children. They provide little guidance or care when a child is emotionally hurt or needs help with a problem.
An uninvolved parent is indifferent to the social-emotional and behavioral needs of their child. This means that they often do not have the rules that apply in the family, and this behavior is especially visible when children enter the classroom.
Pdf) Parenting Styles As Perceived By Parents And Children
This parenting style has little control and support. They do not demand much from their children and do not respond when they need emotional support. They are also very low in structure.
Children of absent parents suffer the most, with cognitive decline, antisocial behavior, attachment problems and even brain abnormalities. The good news is that Dr. Emmy Werner, who researches the recovery of neglected children, believes that all it takes to strengthen a neglected child is a caring adult – a teacher, grandparent or counselor – who will care for them. can take care of. . The path of patience and hope.
Permissive parenting styles are often child-centered. The child runs the house and has no rules or expectations